The Definition of In Vitro Diagnostic
In Vitro Diagnosis (IVD) refers to a diagnostic method that obtains clinical diagnostic information by collecting and examining biological samples, such as blood, saliva, or tissue, to diagnose, treat, or prevent health conditions. In vitro diagnosis is an important source of clinical diagnosis, which can provide important reference indexes for doctors' treatment plans. IVD is an indispensable part of the medical system to ensure human health.
IVD Market Segmentation
Based on the classification of test principles, the IVD market segment can be divided into Microbiology, Clinical Chemistry, Hematology, Coagulation, Immunoassay, Molecular Diagnostics, POCT, etc. Based on the classification of the test product, the IVD market can be divided into reagents, instruments, and services.
Evolution of the IVD
Stage 1:
The invention of the microscope gave rise to some traditional examination methods.
Stage 2:
The development of modern medicine and the discovery of enzyme-catalyzed reactions and antigen-antibody reactions laid the foundation for biochemical and immunodiagnosis, thus in vitro diagnostics are rising and gradually expand during this period.
Stage 3:
The application of DNA double helix structure, monoclonal antibody technology, and macromolecular markers technology promoted the development of molecular diagnostics in vitro diagnosis industry.
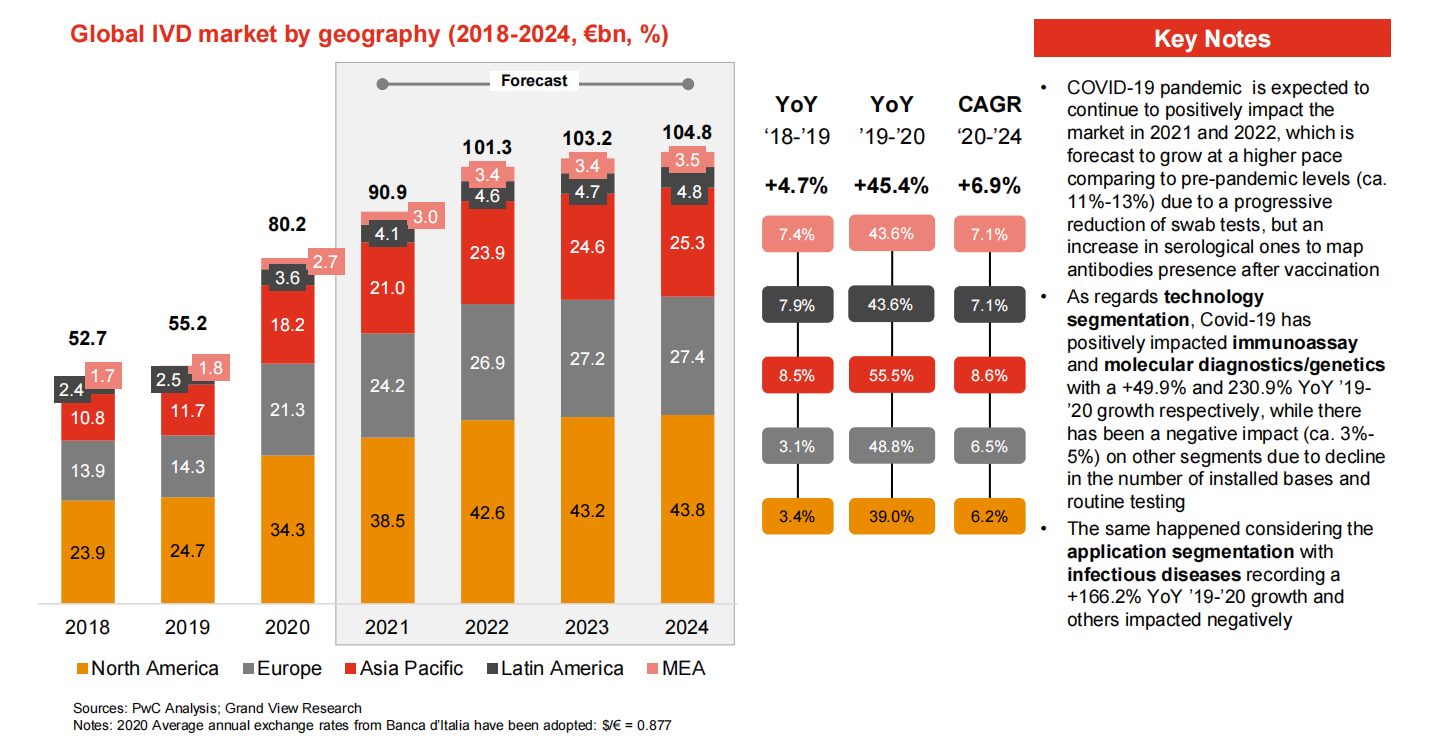
Global IVD Market
Over 70% of the global IVD market is occupied by Europe, North America and Japan. Four main international players are Roche (Switzerland), Abbott (US), Thermo (US) and Siemens (Germany). This four companies had a combined global market share of about 51% in 2017.



.png)




 Business card
Business card Chinese WeChat
Chinese WeChat