In medical terms, "coagulation" is a complex physiological process, which refers to a series of reactions in which blood changes from liquid to solid gel-like blood clots. The main purpose is to stop bleeding and prevent excessive blood loss. The following is a detailed explanation from the aspects of coagulation factors, coagulation process and abnormal coagulation mechanism:
1-Coagulation factors: There are many coagulation factors in the blood, such as factor I (fibrinogen), factor II (prothrombin), factor V, factor VII, factor VIII, factor IX, factor X, factor XI, factor XII, etc. Most of them are synthesized in the liver. These coagulation factors play a key role in the coagulation process, and through a series of activations and interactions, the blood is finally coagulated.
2-Coagulation process: It can be divided into the intrinsic coagulation pathway and the exogenous coagulation pathway. Both pathways eventually converge to the common coagulation pathway to form thrombin, which in turn converts fibrinogen into fibrin to form a blood clot.
(1) Intrinsic coagulation pathway: When the vascular endothelium is damaged and the blood comes into contact with the exposed subendothelial collagen fibers, factor XII is activated, starting the intrinsic coagulation pathway. Factor XI, factor IX, factor X, etc. are then activated in sequence, and finally, on the phospholipid surface provided by platelets, factor X, factor V, calcium ions and phospholipids together form prothrombin activator.
(2) Extrinsic coagulation pathway: It is initiated by the release of tissue factor (TF) by tissue damage. TF combines with factor VII to form a TF-VII complex, which activates factor X and then forms prothrombin activator. The extrinsic coagulation pathway is faster than the intrinsic coagulation pathway and can cause blood to coagulate in a shorter time.
(3) Common coagulation pathway: After the prothrombin activator is formed, prothrombin is activated to thrombin. Thrombin is a key coagulation factor that catalyzes the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin monomers. Under the action of factor XIII and calcium ions, fibrin monomers cross-link to form stable fibrin polymers. These fibrin polymers are interwoven into a network, entrapping blood cells to form blood clots and complete the coagulation process.
3-Abnormal coagulation mechanism: including hypercoagulability and coagulation disorders.
(1) Hypercoagulability: The body is in a hypercoagulable state and is prone to thrombosis. For example, in cases of severe trauma, major surgery, malignant tumors, etc., the activity of coagulation factors and platelets in the blood increases, and the blood viscosity increases, which can easily lead to thrombosis, which may cause serious diseases such as pulmonary embolism, cerebral infarction, myocardial infarction, etc., and endanger life.
(2) Coagulation disorder: refers to the lack or abnormal function of certain coagulation factors in the blood coagulation process, which leads to an increased bleeding tendency. Common causes include hereditary coagulation factor deficiency, such as hemophilia A (factor VIII deficiency) and hemophilia B (factor IX deficiency); vitamin K deficiency, which affects the synthesis of factors II, VII, IX, and X; liver disease, which leads to reduced synthesis of coagulation factors; and the use of anticoagulants, such as warfarin and heparin, which inhibit the coagulation process.
Coagulation plays a vital role in maintaining the normal physiological function of the human body. Any abnormality in coagulation function may have a serious impact on health. In clinical practice, various coagulation tests, such as prothrombin time (PT), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), fibrinogen determination, etc., are often used to evaluate the patient's coagulation function, so as to timely detect and treat coagulation-related diseases.
Beijing Succeeder Technology Inc. (Stock code: 688338), founded in 2003 and listed since 2020, is a leading manufacturer in coagulation diagnostics. We specialize in automated coagulation analyzers and reagents, ESR/HCT analyzers, and hemorheology analyzers. Our products are certified under ISO 13485 and CE, and we serve over 10,000 users worldwide.
Analyzer Introduction
Fully Automated Coagulation analyzer SF-9200 (https://www.succeeder.com/fully-automated-coagulation-analyzer-sf-9200-product) can be used for clinical test and pre-operative screening. Hospitals and medical scientific researchers also can use SF-9200. Which adopts coagulation and immunoturbidimetry, chromogenic method to test the clotting of plasma. The instrument shows that clotting measurement value is the clotting time (in seconds). If the test item is calibrated by calibration plasma, it can also display other related results.
The product is made of sampling probe movable unit, cleaning unit, cuvettes movable unit, heating and cooling unit, test unit, operation-displayed unit, LIS interface (used for printer and transfer date to Computer).
Technical and experienced staffs and analyzers of high quality and strict quality management are the guarantee of manufacture of SF-9200 and good quality. We guarantee each instrument inspected and tested strictly. SF-9200 meets China national standard, industry standard, enterprise standard and IEC standard.
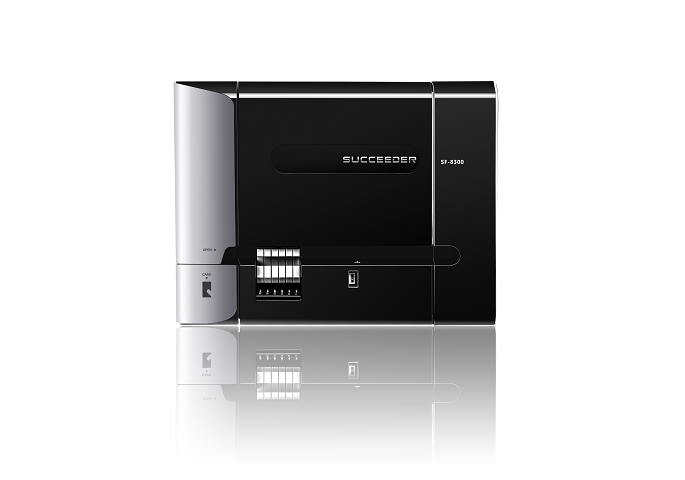
SF-9200
Fully Automated Coagulation Analyzer
Specification
Assay: Viscosity-based (mechanical) clotting, Chromogenic and Immunoassays.
Structure: 4 probes on separate arms, cap-piercing optional.
Test Channel: 20
Incubation Channel: 30
Reagent Position: 60 rotating and tilt positions, internal barcode reading and auto loading, reagent volume monitoring,
multi-vials auto switching, cooling function, non-contact reagent mixing.
Sample Position: 190 and extensible, auto loading, sample volume monitoring, tube auto rotation and barcode reading, 8 separate STAT position, cap-piercing optional, LAS support.
Data Storage: Result auto storage, control data, calibration data and their graphs.
Intelligent Monitoring: On probe anti-collision, cuvette catch, liquid pressure, probe blocking and operation.
Result can be searched by date, sample ID or other conditions, and can be cancelled, approved, uploaded, exported, printed, and can be counted by test quantity.
Parameter Set: Test process definable, test parameters and result-unit settable, test parameters include analysis, result, re-dilution and retest parameters.
Throughput: PT ≥ 415 T/H, D-Dimer ≥ 205 T/H.
Instrument Dimension: 1500*835*1400 (L* W* H, mm)
Instrument Weight: 220 kg








 Business card
Business card Chinese WeChat
Chinese WeChat