-

What causes coagulation problems?
Coagulation may be caused by trauma, hyperlipidemia, and platelets. 1. Trauma: Self -protection mechanisms are generally a self -protection mechanism for the body to reduce bleeding and promote wound recovery. When the blood vessels are injured, the blood intravascular c...Read more -
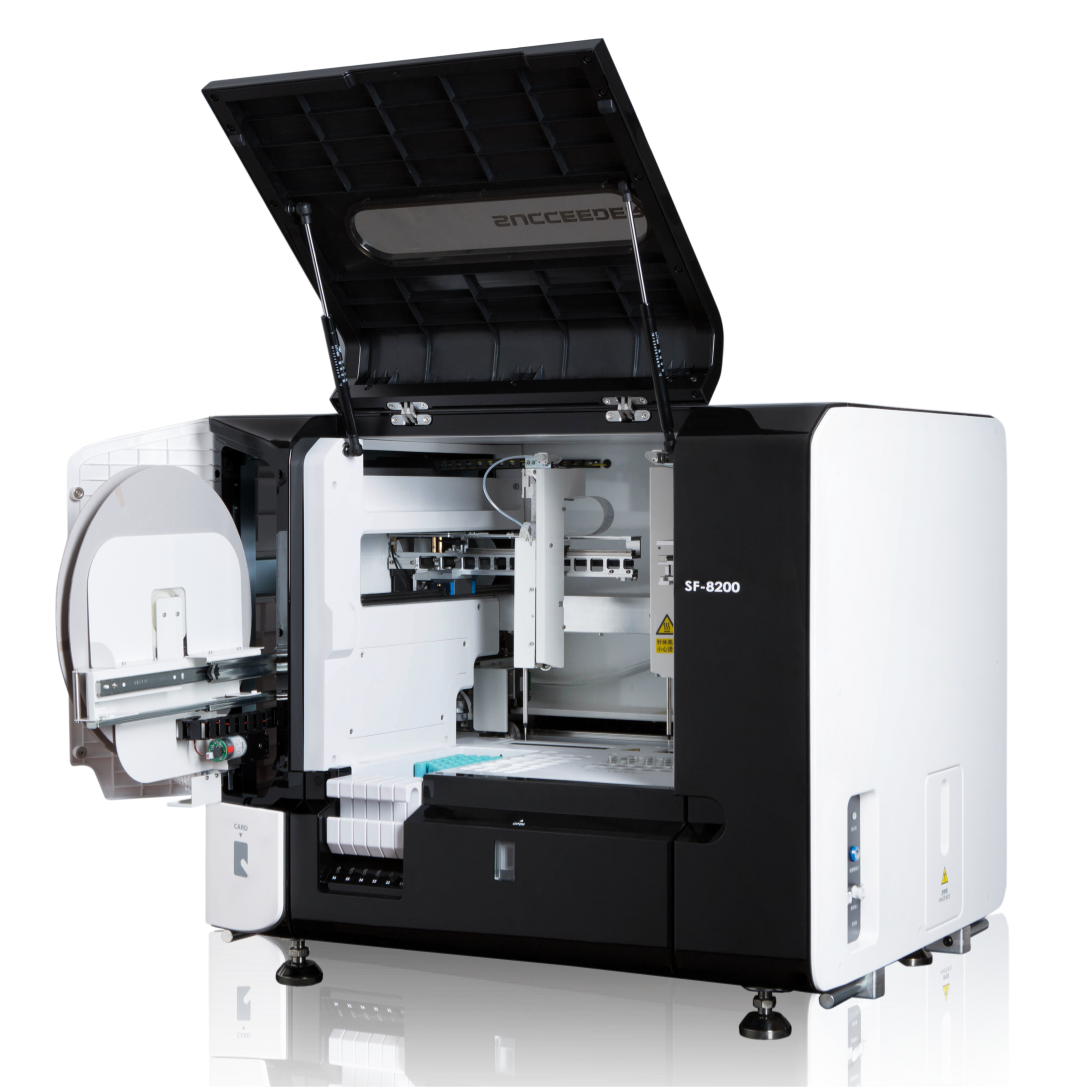

What is a coagulation analyzer used for?
Thrombosis and hemostasis are one of the important functions of blood. The formation and regulation of thrombosis and hemostasis constitute a complex and functionally opposite coagulation system and anticoagulation system in the blood. They maintain a dynamic balance thr...Read more -
What is the action of thrombin and fibrinogen?
Thrombin can promote blood coagulation, play a role in stopping bleeding, and can also promote wound healing and tissue repair. Thrombin is an important enzyme substance in the process of blood coagulation, and it is a key enzyme that was originally converted into fibrin...Read more -
What is the function of thrombin?
Thrombin is a kind of white to gray -white non -crystalline substance, generally frozen -dried powder. THROMBIN is a kind of white to gray -white non -crystalline substance, generally frozen -dried powder. Thrombin is also called coagulation factor Ⅱ, which is a multifun...Read more -
What is the difference between prothrombin time and thrombin time?
Thrombin time (TT) and prothrombin time (PT) are commonly used coagulation function detection indicators, the difference between the two lies in the detection of different coagulation factors. Thrombin time (TT) is an indicator of the time required to detect the conversi...Read more -

What is prothrombin vs thrombin?
Prothrombin is the precursor of thrombin, and its difference lies in its different properties, different functions, and different clinical significance. After prothrombin is activated, it will gradually convert into thrombin, which promotes the formation of fibrin, and t...Read more







 Business card
Business card Chinese WeChat
Chinese WeChat English WeChat
English WeChat